This article explains the term “broad-based disc herniation” commonly found on the reports of the magnetic resonance (MR) and computed tomography (CT) images of the spine.
Doctors often use nonstandard terms, such as “broad-based disc bulge” or “broad-based disc prolapse,” which may or may not mean broad-based disc herniation. The most reliable way to find out the real meaning of these terms in a particular CT or MR image report is to contact the doctor who has written the report.
What is the spinal disc?
The spinal or intervertebral discs are cartilages between the bones (vertebrae) in the spine (Picture 1).
What are a disc bulge and disc herniation?
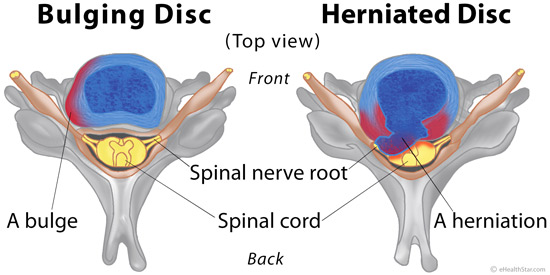
A disc bulge is a condition in which a portion of the disc extends beyond its normal limits but the inner part of the disc (nucleus pulposus) remains completely within the fibrous ring (annulus fibrosus) (Picture 2) [1]. In a more severe condition called a disc herniation, a part of the disk center is squeezed out through a crack in the fibrous ring (Picture 2).
What does a broad-based disc herniation mean?
In a broad-based herniation, a part of the soft disc center breaks through 25-50% of the disc’s circumference [1]. For comparison, a focal herniation occupies less than 25% of the disc’s circumference [1].
What are symptoms of a broad-based disc herniation?
Symptoms, which are much less common in broad-based than in focal disc herniation, can include pain in the neck, lower back, arm or leg.
What is a central or posterior broad-based disc herniation?
A central or posterior disc herniation points to the spinal cord.
What are a minimal, shallow and moderate broad-based disc bulge?
The terms minimal, mild, small, shallow and moderate broad-based disc bulge refer to various stages of a disc bulge that rarely cause any symptoms.
What is a broad-based disc osteophyte complex?
The term “disc osteophyte complex” also known as “hard disc” or “chronic disc herniation” refers to a combination of one or more disc herniations and bone spurs (osteophytes) in the neck spine [2]. The condition can cause a pinched nerve with pain in the neck, upper back, shoulder or arm pain.
- References
- Fardon DF et al, 2014, Lumbar disc nomenclature: version 2.0: Recommendations of the combined task forces of the North American Spine Society, the American Society of Spine Radiology and the American Society of Neuroradiology The Spine Journal
- Disc osteophyte complex Radiopedia

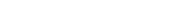
Doctor answers on Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and More: Dr. Saponaro on broad based disc bulge: Herniated disc‘s can often be symptom free. And quite often pain …
I need some help, I’ve had an MRI done, I’m worried my gp has not got the knowledge or has a lack of knowledge in this specific area
Yes?