Trapezius Muscle Location
The trapezius is the biggest shoulder muscle. It extends from the neck and chest part of the spine to the shoulder blades on both sides.
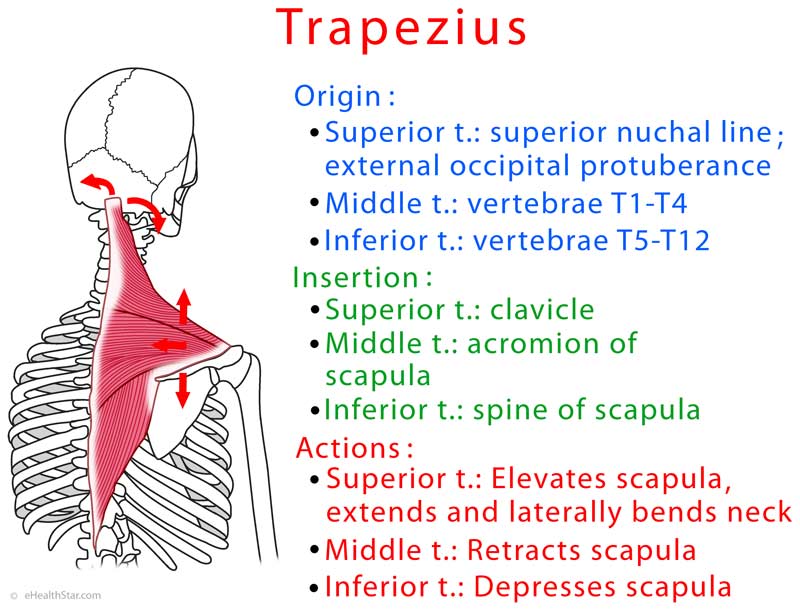
Origin
- Superior (upper, descending) trapezius: medial third of superior nuchal line; external occipital protuberance, nuchal ligament
- Middle (transverse) trapezius: spinous processes of the vertebrae T1-T4
- Inferior (lower, ascending) trapezius: spinous processes of the vertebrae T5-T12
Insertion
- Superior trapezius: lateral third of the clavicle
- Middle trapezius: acromion
- Inferior trapezius: spine of the scapula
- Reference: [1]
Functions (Actions)
- Upper trapezius elevates and upwardly rotates the scapula and laterally flexes the head; the right and left trapezius together extend the neck (backward).
- Middle or transverse trapezius retracts the scapula (bring it close to the spine), together with rhomboid major and major.
- Lower or ascending trapezius depresses and upwardly rotates the scapula.
- Reference: [1]
Innervation
- Motor fibers: accessory nerve (cerebral nerve XI) [1]
- Pain and proprioception: spinal nerve roots C3 and C4 [1]
Blood Supply
- Transverse cervical artery [1]
Picture 1. Trapezius anatomy: origin, insertions, actions
Video 1. Trapezius anatomy: origin, insertion, action
Trapezius Pain
Acute Trapezius Pain
Acute pain in the trapezius muscle can be caused by a contusion, strain or tear.
Trapezius Strength Test
Decreased strength in the trapezius speaks for an injury of the trapezius tendon or the related nerves (spinal nerve roots C3 or C4 due to a herniated disc).
Th test consists of 3 parts (Video 2):
- Upper trapezius. Sit down, raise the shoulders and extend the neck against the pressure of the examiner’s hand put on the back of your head.
- Middle trapezius. Retract the shoulder blades (bring them together) against the pressure of the examiner’s hands put near the middle borders of your shoulder blades.
- Lower trapezius. Pull the shoulder blades downward against the pressure of the examiner’s hands put at the bottom of your shoulder blades.
Video 2. Trapezius muscle strength test
Chronic Pain: Trapezius Myalgia, Spasm, Repetitive Stress Injury
Trapezius myalgia develops due to increased tension in the upper trapezius and is more common in women than in men [2].
Causes include [2]:
- Repetitive arm and shoulder movements in assembly work, swimming, rowing, weightlifting, tennis, driving or sewing without arms being supported
- Holding the phone between the ear and shoulder
- Playing an instrument, such as violin or flute
- Poking the chin, bending forward or armrests that are too high during sitting (computer work)
- Scoliosis, leg length discrepancy, limping, using a cane
- Herniated disc (C2-C3 or C3-C4) in the neck spine (cervical radiculopathy)
- Psychological stress, anxiety
Symptoms can include tenderness, pain, stiffness and tingling in the shoulders and back of the neck, nausea and anxiety [2]. Chronic pain can become worse after a period of inactivity [2].
Signs. A doctor may be able to identify muscle knots. Applying pressure to the muscle knots that act as trigger points can trigger a headache behind the eyes, in the temples and at the back of the head (myofascial pain) [2].
The following treatment methods can be effective [2]:
- Rest from the activities that cause pain
- Ice packs for 10 minutes several times a day in the first 48 hours after the pain onset
- Painkillers, such as ibuprofen
- Injections of steroids and local anesthetics for short-term pain relief
- Dry needling
- Ischemic compression
- Friction massage
- Strengthening exercises
- Arm cycling or cycling with relaxed shoulders
Prevention:
- Avoid activities that cause you more anxiety than peace.
- Concentrate on work goals rather on work difficulty.
- Correct the sitting position.
Stretching Exercises to Release Tight Trapezius
Three simple exercise to release trapezius pain you can due during work: shoulder blade retraction (scapular pinches), shrugging and bending the head toward the hip (Video 3).
Video 3. Causes of trapezius pain and releasing exercises
Trapezius Strength Test
Decreased strength in the trapezius speaks for an injury of the trapezius tendon.
Th test consists of 3 parts (Video 3):
- Upper trapezius. Sit down, raise the shoulders and extend the neck against the pressure of the examiner’s hand put on the back of your head.
- Middle trapezius. Retract the shoulder blades (bring them together) against the pressure of the examiner’s hands put near the middle borders of your shoulder blades.
- Lower trapezius. Pull the shoulder blades downward against the pressure of the examiner’s hands put at the bottom of your shoulder blades.
Video 3. Trapezius muscle strength test
- References
- Trapezius University of Washington, Department of Radiology
- Trapezius myalgia Physiopedia