What is Guyon’s canal?
Guyon’s Canal is a canal on the palmar and pinky side of the wrist through which the ulnar nerve, artery and vein run.
Other names: Guyon’s tunnel, ulnar canal, ulnar tunnel
Location
Guyon’s canal is about four centimeters long; it starts at the proximal end (toward the body) of the transverse carpal ligament and ends at the distal end (toward the fingers) of the hypothenar muscles.
Borders
Limits of Guyon’s tunnel (Picture 1) 1:
- Floor: transverse carpal ligament
- Roof: palmar carpal ligament
- Ulnar (medial) border: pisiform bone
- Radial (lateral) border: the hook of hamate bone
Picture 1. Guyon’s canal (left hand from the palmar side)
Yellow: the ulnar nerve and its sensory and motor branch; Red: The ulnar artery;
The palmar carpal ligament and pisohamate ligament cover the ulnar nerve, but in the image, they are cut.
The space beneath these two ligaments is Guyon’s canal.
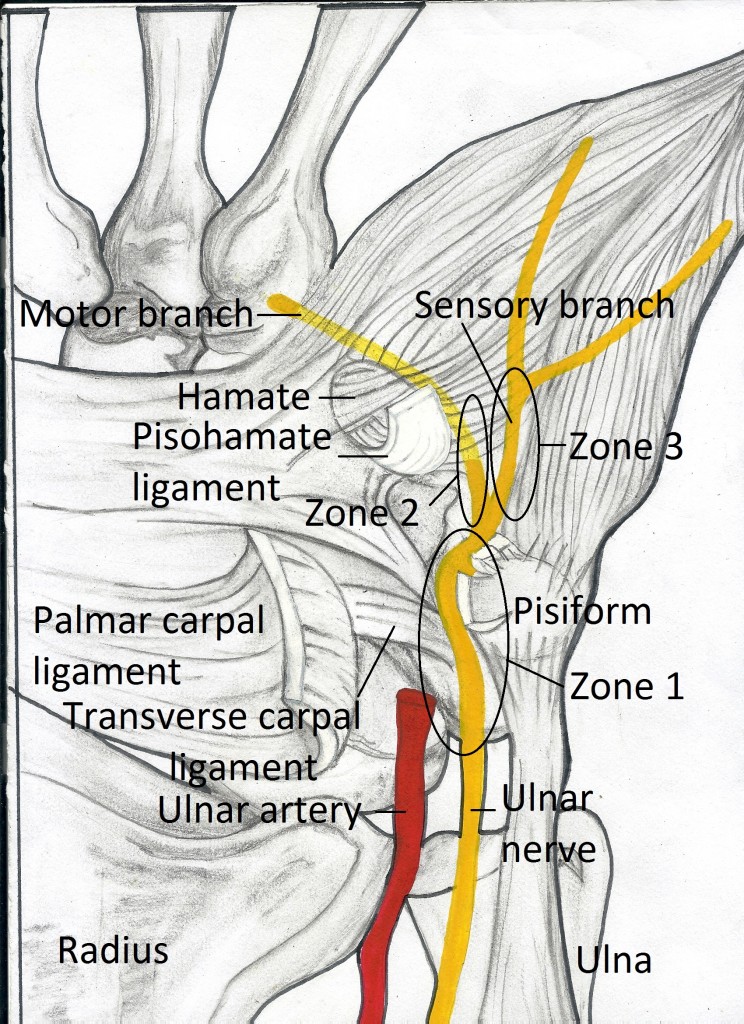
Guyon’s Canal Zones
(See Picture 2)
- Zone 1 can result in both impaired sensitivity (tingling, numbness) and impaired muscle function (muscle weakness and atrophy)
- The isolated damage of the nerve in the Zone 2 (the motor branch of the nerve) results in the weakness of the thumb and clawing of the 4th and 5th finger, but the sensitivity remains intact.
- The isolated damage of the ulnar nerve in the Zone 3 (the sensory branch of the nerve) results in tingling and numbness in the 4th and 5th finger, but the strength of the muscles in the hand is not affected.
Picture 2. Guyon’s canal zones
The damage of the ulnar nerve in different zones
results in different symptoms.
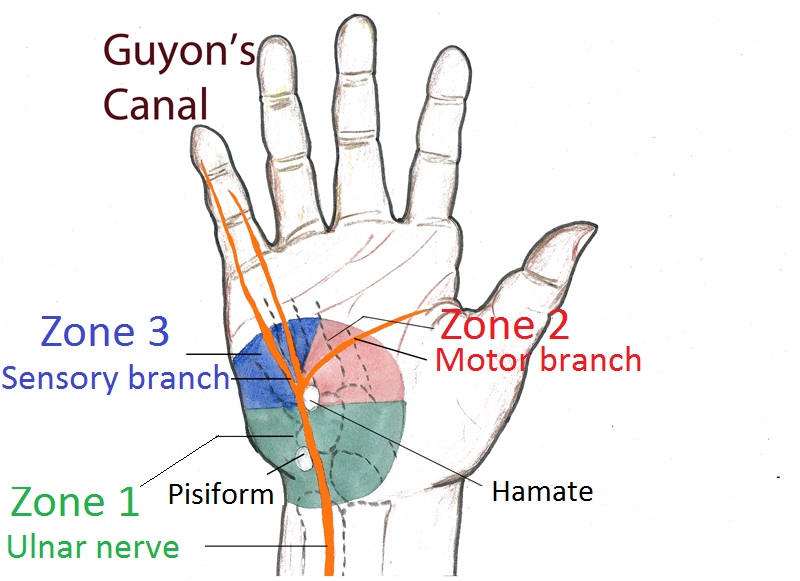
Picture 3. Guyon’s canal and carpal tunnel (right hand)
The Guyon’s canal is above the carpal tunnel.
The Guyon’s canal is on the ulnar side of the wrist, while carpal tunnel lies more centrally.
Physiology
The part of the ulnar nerve that travels through the Guyon’s canal enables 8,9:
- Sensitivity of the skin on the palmar side of the little finger and adjacent half of the ring finger and the related part of the palm
- Moving the thumb toward the palm
- Spreading the fingers.
Pathophysiology
The Guyon’s canal is a site where an ulnar neuropathy due to ulnar nerve entrapment can develop.
Guyon’s Canal Syndrome
Guyon’s canal syndrome is a combination of symptoms which result from the compression of the ulnar nerve within the canal.
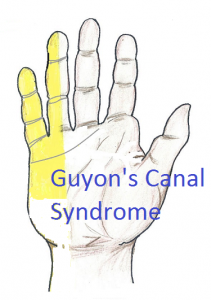
Picture 4. Guyon’s canal syndrome
Yellow: the area with tingling and numbness
- References
- Relevant Surgical Exposures, y.2008, p.11 (Anatomy)
- Physio-pedia.com (Signs of ulnar nerve entrapment)
- Eorthopod (Guyon’s canal syndrome treatment)

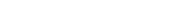
the area with tingling an numbness needs to be adjusted, as the superficial branch of ulnar nerve innervates the palmar aspect of 1 and half medial fingers. Other than that, great explanations!
No james is right…..
Corrected.
Please adjust the borders of the canal. The ulna is medial and the radius is lateral.
James, it is a left hand from the palmar side, so ulna is on the left side and radius on the right.
thank,s